容易想象的是,路怒症(Road rage)跟车祸有明显的相关性[1],Dr. Leon James在1997年的国会证词中指出,路怒症是美国交通事故的第一大元凶[2]。但是路怒症并没有被收录进 精神疾病诊断与统计手册 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th edition, DSM-5)[3],因其诊断量化标准无法取得统一。
路怒症一般被认为是人在压力下的正常反应[4],比如面对交通堵塞、其他人不友好的驾驶行为[5]、工作和生活的困难等。这些压力激发了人身体的 战斗或逃跑反应 (Fight-or-flight response)[6],改变人体神经元的离子通道控制状态[7, 8],引发一系列的生理反应。包括增强身体的力量,减少对四肢的供血以应对可能的危险。同时也会改变精神状态,使人失去理性(大脑皮层高级功能区域被抑制),容易被激怒,引发暴力行为。
有些患有其他精神疾病的人更容易爆发路怒症症状,比如 间歇性暴发性精神障碍 (Intermittent explosive disorder, IED)。该疾病患者比常人更 紧张、提心吊胆、不安全和自卑 ,因此会出现以下症状
1、多次出现不可控制的发怒,结果导致严重的攻击行为或砸毁财物的行为;
2、患者的发怒与其心理社会应激源程度不相符,即使轻微的刺激也可以导致患者发怒;
同时患者在爆发之后,又会非常的愧疚自己爆发之时的暴力行为,因此该病经常被误认为仅仅是性格火爆而已。
与正常人相比, 间歇性暴发性精神障碍 (已被DSM-5收录)患者表现为对识别和理解他人的面部情绪表情存在困难:
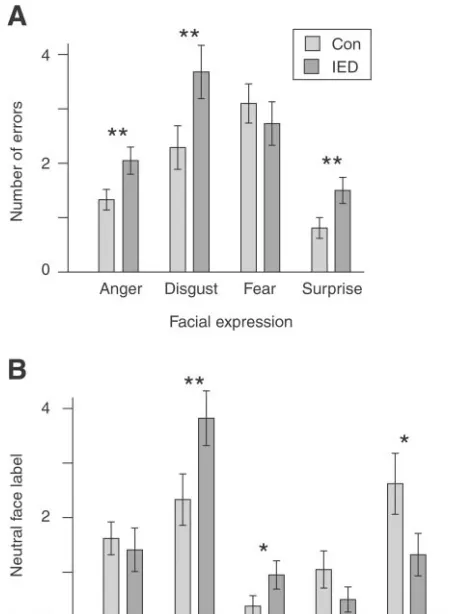
同时行事更加鲁莽/非理性,即使是在未发病状态[9]:
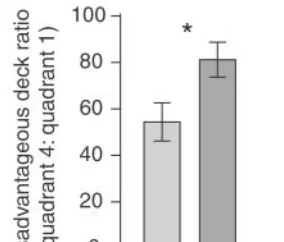
这显示TA们的前额叶功能受损或不全。该疾病 患者除了容易爆发路怒症外,还容易对配偶/家人实施家暴行为 。需要注意到的是,该疾病( 间歇性暴发性精神障碍 )的发病率并不低,在 5%到7% 之间[10],是路怒症的主要诱因之一。患有该疾病的驾驶者是路面上的定时炸弹,碰到交通堵塞或其他人的鲁莽行为,非常容易被激怒。因此, 在路面上碰到路怒症爆发并不是小概率事件,多次爆发路怒症者很可能也是一个家暴者 。
目前,大部分路怒症的处理/应对策略在认知范畴,即 教导驾驶者关于暴力驾驶的危险,应对和处理自己的压力等 。同时由于以上提到的 路怒症跟家暴的关系,使用应对家暴的策略也能一定层度上的减少路怒症出现 [11],包括发展和寻找同理心/同情心等。同样由于路怒症跟间歇性暴发性精神障碍的紧密关系,有些研究者建议 在驾照考试中增加间歇性暴发性精神障碍的诊断内容,让诊断出的患者参加额外的压力应对培训以减少路怒症的出现 [12]。
--------
[1] Wells-Parker, Elisabeth, et al. "An exploratory study of the relationship between road rage and crash experience in a representative sample of US drivers." Accident Analysis & Prevention 34.3 (2002): 271-278.
[2] James, Leon. "Congressional testimony on aggressive Driving." (1997).
[3] DSM-5 American Psychiatric Association. "Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders." Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing (2013).
[4] Gerrig, Richard J., et al. Psychology and life . Pearson Higher Education AU, 2011.
[5] Britt, Thomas W., and Michael J. Garrity. "Attributions and personality as predictors of the road rage response." British Journal of Social Psychology 45.1 (2006): 127-147.
[6] McDonald, S. Psychology of Aggressive Driving and Road Rage (2002).
[7] Jansen, Arthur SP, et al. "Central command neurons of the sympathetic nervous system: basis of the fight-or-flight response." Science 270.5236 (1995): 644-646.
[8] Fuller, Matthew D., et al. "Molecular mechanism of calcium channel regulation in the fight-or-flight response." Science signaling 3.141 (2010): ra70.
[9] Best, Mary, J. Michael Williams, and Emil F. Coccaro. "Evidence for a dysfunctional prefrontal circuit in patients with an impulsive aggressive disorder." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99.12 (2002): 8448-8453.
[10] Kessler, Ronald C., et al. "The prevalence and correlates of DSM-IV intermittent explosive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication." Archives of general psychiatry 63.6 (2006): 669-678.
[11] Marano, H.. 「The solution to road rage? Find compassion」, in Psychology Today, 18 Feb (2003).
[12] Asbridge, Mark, Reginald G. Smart, and Robert E. Mann. "Can we prevent road rage?." Trauma, violence, & abuse 7.2 (2006): 109-121.










