首先這是維基的介紹:
The Gerchberg–Saxton (GS) algorithm is an iterative algorithm for retrieving the phase of a pair of light distributions (or any other mathematically valid distribution) related via a propagating function, such as the Fourier transform, if their intensities at their respective optical planes are known.另外我之前做的一個關於計算全像圖的小project提到了GS演算法,按照維基裏面的圖,簡單說一下我的理解。
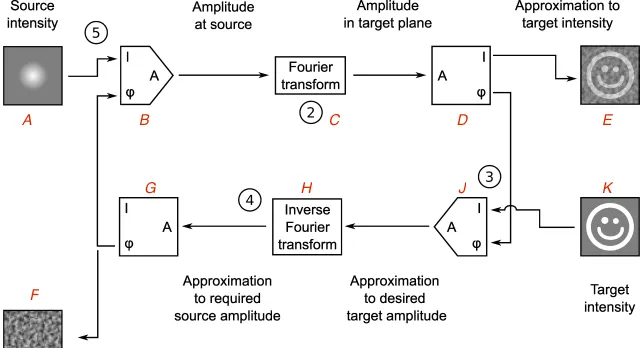
按照圖片,我們想在光源A(通常是平行光)的基礎上疊加相位B,從而經過傅立葉變換C(也就是透過凸透鏡)後在平面D上得到如圖K所示的又亮(intensity efficient) 又均勻(low variance)的笑臉。
GS演算法就是根據想要的影像K求出B上面應該疊加什麽樣的相位也就是所謂的計算全像圖F,具體思路如下:
(1) 離散化 :設B上面每個像素點的相位是\phi_j ,D上面每個像素點的復振幅為V_m . GS演算法的目的是透過改變\phi_j 使\sum_m |V_m| 最大。也就是說所有像素點亮度的和最大,從而達到「明亮」的目的。
(2) 最佳化 :根據上面的思路我們可以計算出\phi_j({|V_m|}) .為了讓所有人都可以看懂,我不把公式放上來,剛興趣的話見文末的參考文獻。
(3) 叠代 :現在問題來了。要想求出最佳化的\phi_j 我們需要V_m ;但是V_m 又是透過\phi_j 決定的。這樣的話怎麽辦呢?解決方法是先給\phi_j 賦一個初值,得到的V_m 肯定滿足不了(1)中的要求。我們就把這個V_m 帶入(2)中最佳化公式再求出\phi_j ,然後進行叠代計算。經過有限步數之後結果會收斂,也就是說每次計算出的V_m 差別都不太大。這時候我們就求出想要的相位圖了。
基本思路就是這樣。其實還有很多類似的演算法用於求\phi_j 。不同的只是在第一步離散化的時候我們想要什麽最大。GS演算法是要\sum_m |V_m| 最大,你也可以讓\sum_m Re(V_m) 最大,等等。
現在理解文首那句解釋了麽?
參考文獻:
Di Leonardo, Roberto, Francesca Ianni, and Giancarlo Ruocco. "Computer generation of optimal holograms for optical trap arrays." Optics Express 15.4 (2007): 1913-1922.











